Erectile dysfunction (impotence)
Erectile dysfunction (impotence)
Definition: Erectile dysfunction is a sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to maintain or develop an erection of the penis sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance.
According to data from National Institute of Health of year 2002 about 15 -30 million men in USA suffer from erectile dysfunction.
According to the research of Massachusetts Male aging Institute, 52% of men after age 40 suffer from erectile dysfunction, but only a small percentage of them are seeking for medical assistance.
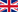
Erection phenomenon.
For erection phenomenon to happen, it is necessary that some complex physiological and psychological preconditions take place:
Psychogenic status - a man must have the desire to make coitus, he shouldn’t feel depressed, troubled or stressed.
The blood flow in penis (the afflux of blood has to be intensive and the outflow of blood can not be disturbed).
Blood has to contain androgens (testosterone) - in normal proportion to other hormones and in unbounded form.
Nerve fibers can not be irritated or damaged in other ways.
Neurotransmitters - the concentration of impulse transferring mediators must be at normal levels
Enzymes - ferments that regulate the speed of chemical reactions, they must be in a sufficient concentration.
In a relaxed state the blood afflux to lacunes in penis is limited and they are empty, and also the outflow of these is completely smooth.
In erected condition helicon and other penis arteries gets enlarged, what results filling lacunes whit blood, compensating outflow arteries and veins - in the furthering processes penis changes from tumescence phase to erectile phase.
Causes:
Psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Takes place in approximately 20% of all cases of impotence. The most frequent symptoms are uncertainty and fear, fear of sexual failure (if there was any) and permanent depression. Chronic fear produces transmitters – these are neuromediators that cause spasms of blood vessels in small pelvis (pelvis minor) and this, in turn, leads to impotence.
It is typical that depression is decreasing libido.
Physical or organic erectile dysfunction – takes place in approximately 80% of all cases of erectile dysfunction.
1) Genesis of blood vessels:
a) Diabetes. About 35% -50% of all patients with diabetes are complaining about an erectile dysfunction. The main reasons are: high level of glucose in blood reduces the level of testosterone what causes damaging of blood vessels and nerves – micro and macro angiopathy.
b) Hypertension - High blood pressure causes damaging of blood vessels in penis, micro splits, sclerotization, stricture. Patients with hypertension have a reduced level of testosterone for about 12%; the volume of semen is also reduced. Also, it is proved in many studies that long-term patients with hypertension have reduced NO (nitric oxide) ions production, which participate in the processes of enlargement of blood vessels in penis.
c) Atherosclerosis together with high level of cholesterol. It is proved in some experiments that 70.6% of the 215 erectile dysfunction patients have increased level of cholesterol - above 5.17 mmole/l
d) Heart diseases
e) Smoking
f) Weakened general blood circulation
2) Neurological disorders:
a) Cerebral contusion;
b) Cerebral blood circulatory disorders;
c) Multiple sclerosis;
d) Alzheimer's disease;
e) Parkinson's disease;
f) Spinal cord injuries and due to many illnesses it causes - intervertebral disc hernia ;
g) Epilepsy;
h) Dissection of retroperitoneal lymph node ;
i) Diabetes;
j) Pelvic surgeries.
a. General prostatectomy surgery causes erectile dysfunction in 10% of all cases;
b. Radical prostatectomy in 40% -100% of all cases leads to erectile dysfunction.
As a result of illnesses of the spinal cord and nerve fibers, the transmission of nerve impulses from cerebral cortex to the centre of erection in spinal cord and from penis receptors to the spinal cord is disturbed.
3) Hormonal disorders:
a) Hypogonadism - causes around 5% of all impotencies. Illnesses of testes and appendages with the reduced level of testosterone as well as with the increased level of follicle gonadotrophic hormone;
b) Thyroid diseases with hormonal disorders - hyperthyrosis and hypothyroidism (representing approximately 6% of all impotencies);
c) Pituitary gland illnesses with increased level of prolactin;
d) Hormonal disorders of adrenal gland. Cushing syndrome.
4) Kidney illnesses – as the result of kidney disorders, organism starts intensify to accumulate various toxic substances - kreatine, urea and others, what causes toxic damage of testicle and reduced testosterone secretion. And additionally - the damaging of nerves - uremic neuropathy..
5) Liver illnesses –Because of the liver damages develops hypogonadism, testicular atrophy. Usually observes decreased level of general testosterone, but especially the level of independent testosterone, increased level of estradiol, gynecomastia, reduced secondary hairiness, infertility and erectile dysfunction.
6) Prostate cancer. In this case, the main reason of impotence is medical manipulations - chemotherapy, irradiation and surgical interventions.
7) Medicines - more than 200 trade names - (several cardiologic preparations, some antifungal drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, and prostate cancer products, some of the gastric acid-lowering drugs)
8) Life style
a) Alcohol. For young people at the early stage alcohol acts as a libido stimulator, because of the fact that psychogenic tension is removed, but then starts many negative effects, in particular, if consumed alcohol level reaches 150 -250 ml, libido and erection is worsening. Alcohol inhibits cholesterol conversion to testosterone. Alcohol intoxication reduces testosterone levels for about 25% and it lasts for 10 -16 hours even after the level of alcohol in blood has reached normal concentration. Alcohol also causes problems to reach orgasm - patients complain about the inability to achieve orgasm, especially in case of chronic alcoholism. Explanation is that the alcohol in large doses cause’s damages of subcortical brain structures, specifically – damages of limbic structures.
b) Drugs - heroin, marijuana, cocaine. The pleasure of taking drugs for drug users is similar to an orgasm, and therefore drug users have no desire to engage in sex. The use of heroin and methadone by men reduces the level of producing gonadotropin LH (luteinizing hormone) till 95% of all men and then the reducing of testosterone production in testicles, which causes very low libido and erectile dysfunction.
c) Smoking. It causes vascular damage - narrowing of blood vessels and deepening atherosclerosis, which is already essentially irreversible process, as well as the reduction of testosterone. Smoking men for about 40% more often state dysfunction. If a man smokes for 5 years 20 cigarettes per day, then 15% of these men are getting developing vascular occlusion which is followed by impotence. But by smoking for 20 years about 20 cigarettes per day, 72% of men are developing severe atherosclerotic plaques.
d) Sedentary and immobile lifestyle. It goes hand in hand with cardiovascular disorders and obesity.
e) Cycling may be a risk factor for erectile dysfunction and infertility. Several studies have shown that for men after 40 years long-term rides with a bicycle promotes erectile dysfunction, which is explained with the narrow bicycle seat that pressures blood vessels and nerves in the root of penis, although in this case there is so-called “stealing phenomenon” – by great physical strains oxygen is intensively consumed for feeding muscles and there is not enough oxygen for genitals - men are getting fibrotic formations in their genitals.
9) Alimentary factors:
a) Decreased quantity of protein in serum. Scientists have proved that those men who live on a diet rich of animal protein have the total level of testosterone higher than those, who eat only vegetarian products.
b) Zinc deficiency. Zinc is involved in many important biochemical processes, and it has the particular importance to the child's sexual maturation during its growth. Zinc promotes normal prostate functioning, participates in testosterone synthesis in men’s organism.
10) Penile disorders
a) Peyronie's disease – in this case tunic albuginea gets damaged and therefore there is no complete arterial reflux closing.
b) Priapism –painful lasting erection.
c) Penile anatomical abnormalities.
11) Infectious diseases:
a) Immune Deficiency Syndrome - (AIDS);
b) Trypanosomiasis;
c) Tuberculosis;
12) Irritated processes of the testicles, prostate, testis appendage, seminal vesicle;
13) Obesity. Increased body mass index is going hand in hand with decreased testosterone level and increased level of estradiol. Obesity contributes increasing of cholesterol levels, which, in turn, causes atherosclerosis and circulatory disorders of blood vessels in small pelvis.
14) Age. Andropause. By ageing, men get gradual, slow decreasing of sex hormones. It begins around the age of 30-40 and continues to fall by 1-2% per year. Level of cholesterol is growing, which contributes to the development of vascular atherosclerosis, blood vessel blockage and, as a consequence, to impotence.
a) Adenoma of prostate is guiding men in andropause.
Treatment of erectile dysfunction:
To make treatment effective, the main principal is to treat the underlying cause, that caused or contributed to impotence and, therefore, the range of applied medications can be very wide and varied.
Also it is very important to cancel or change all the medicines that contribute to the impotence.
1. Psychotherapeutic methods: hypnosis, Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP), psychoanalysis.
2. Life style correction – a diet, physical activity, sex rhythm recommendations, quitting smoke.
3. Oral treatment:
a. Use of medicine for expanding blood vessels (Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors)
b. Therapy for correcting hormonal level
4. Intra - urethral injections – special candles, which cause an erection, are being inserted in the urinary canal in penis.
5. The use of vacuum pump in the combination with a special tension ring - a man places his penis in a special cylinder; the cylinder is equipped with an air-pumping device. Air gets pumped away from a cylinder and creates vacuum, which causes an artificial erection. After that the lower end of penis is imposed and tightened with a special tag, which prevents the blood flowing out of the penis; then the cylinder is removed and penis can be used for sexual activities.
6. Intravenous treatment – medicines are inserted into cavernous body.
7. Surgical methods
a. Surgeries for blood circulation disorder correction (in practice are not used because of the high effectiveness of Phosphodiesterase inhibitors);
i. Improvement of arterial flow;
ii. Operations for correcting (reducing) venous reflux .
b. Phallus prosthetics - Penile implants are artificial devices, which are implanted into penis to secure its erection. There are two types of such kinds of devices:
i. Inflatable or hydraulic implants, which provide an erection;
ii. Semirigid implants - in this case, penis is in a permanent rigid position.
08.06.2009.yer dr. Orbidāns Jānis